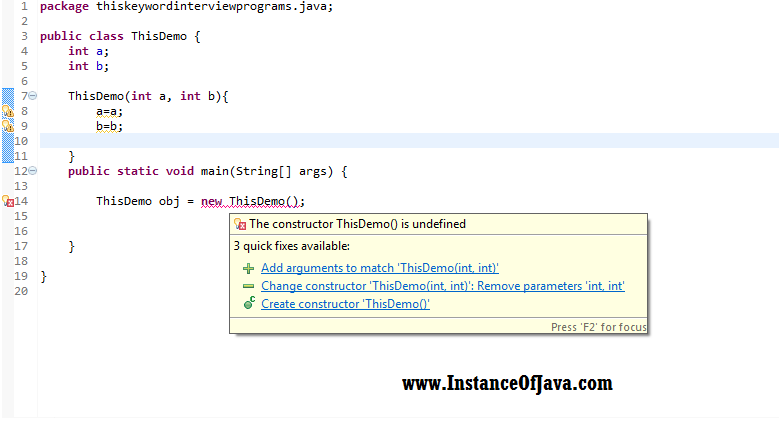
Basic Java Example programs
java interview programs
- We have a Letter or a word then we need add some letters to it and need to find out shortest palindrome
- For example we take "S": S will be the shortest palindrome string.
- If we take "xyz": zyxyz will be the shortest palindrome string
- So we need to add some characters to the given string or character and find out what will be the shortest palindrome string by using simple java program.
Java example Program to find out shortest palindrome of given string - package shortestpalindromeexample.java;
- import java.util.Scanner;
-
- public class ShortestPalindromeDemo {
-
- public static String shortestPalindrome(String str) {
-
- int x=0;
- int y=str.length()-1;
-
- while(y>=0){
- if(str.charAt(x)==str.charAt(y)){
- x++;
- }
- y--;
- }
-
- if(x==str.length())
- return str;
-
- String suffix = str.substring(x);
- String prefix = new StringBuilder(suffix).reverse().toString();
- String mid = shortestPalindrome(str.substring(0, x));
-
- return prefix+mid+suffix;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
-
- System.out.println("Enter a String to find out shortest palindrome");
-
- String str=in.nextLine();
-
- System.out.println("Shortest palindrome of "+str+" is "+shortestPalindrome(str));
-
- }
-
- }
- Enter a String to find out shortest palindrome
- java
- Shortest palindrome of java is avajava
Core java Interview Questions
java Collections interview Questions
- Famous java interview question: difference between collections and collection in java
- Major difference between Collection and Collections is Collection is an interface and Collections is a class.
- Both are belongs to java.util package
- Collection is base interface for list set and queue.
- Collections is a class and it is called utility class.
- Collections utility class contains some predefined methods so that we can use while working with Collection type of classes(treeset, arraylist, linkedlist etc.)
- Collection is base interface for List , Set and Queue.
Collection vs Collections- public interface Collection<E>
- extends Iterable<E>
- public class Collections
- extends Object
- Collections utility class contains static utility methods so that we can use those methods by using class name without creating object of Collections class object
- Lest see some methods of Collections class.
- addAll: public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c,T... elements)
- reverseOrder: public static <T> Comparator<T> reverseOrder()
- shuffle: public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
- sort:public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)
How to Relate Collection and Collections
- ArrayList is a Collection type of class means it is implementing Collection interface internally
- Now lets see a java example program to sort ArrayList of elements using Collections.sort() method.
- public class ArrayList<E>
- extends AbstractList<E>
- implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
1.Basic Java example program to sort arraylist of integers using Collections.sort() method- package com.javasortarraylistofobjects;
-
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.Iterator;
-
- public class SortArrayListExample{
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- //create an ArrayList object
- ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
-
- //Add elements to Arraylist
- arrayList.add(10);
- arrayList.add(7);
- arrayList.add(11);
- arrayList.add(4);
- arrayList.add(9);
- arrayList.add(6);
- arrayList.add(2);
- arrayList.add(8);
- arrayList.add(5);
- arrayList.add(1);
-
-
- System.out.println("Before sorting ArrayList ...");
- Iterator itr=arrayList.iterator();
-
- while (itr.hasNext()) {
-
- System.out.println(itr.next());
-
- }
-
-
- /*
- To sort an ArrayList object, use Collection.sort method. This is a
- static method. It sorts an ArrayList object's elements into ascending order.
- */
- Collections.sort(arrayList);
-
- System.out.println("After sorting ArrayList ...");
-
-
-
- Iterator itr1=arrayList.iterator();
-
- while (itr1.hasNext()) {
- System.out.println(itr1.next());
-
- }
-
-
- }
- }
Output:- Before sorting ArrayList ...
- 10
- 7
- 11
- 4
- 9
- 6
- 2
- 8
- 5
- 1
- After sorting ArrayList ...
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Basic Java Example programs
Core java Interview Questions
- To find missing numbers in an array first we need to make sure that array is sorted.
- After sorting we need to check that array each element with next element then we can find the difference.
- if Array is not sorted :To sort array use Arrays.sort(array);
- If difference is 1 then no need to do any thing because numbers are in order.
- If difference is not equal to 1 then we need to print all those numbers or pick those numbers and place it in one array.
- this would be the logic to find missing numbers in an array
- Here there may be a chance of array not starts with 1 then we need to check first itself whether array starts with 1 or not if not we need to print 1 to starting element of array.
- for example int a[]={4,5,6,8}; then we need to print 1 2 3 7.
Lets see a java example program to find missing numbers in an array.- package arraysInterviewQuestions;
- public class PrintMissingNumbers {
-
- private static void findMissingNumber(int[] number){
-
- // take max length as last number in array
- int k[] = new int[number[number.length-1]];
-
- int m=0;
-
- if(number[0]!=1){
- for (int x = 1; x < number[0]; x++) {
- k[m] = x;
- m++;
- }
- }
-
- for (int i = 0; i < number.length -1; i++) {
-
- int j = i+1;
- int difference = number[j] - number[i] ;
-
-
- if(difference != 1 ){
-
- for (int x = 1; x < difference; x++) {
-
- k[m] = number[i] + x;
- m++;
-
- }
-
- }
- }
-
- System.out.println("missing numbers in array ::");
-
- for (int l = 0; l < m ; l++) {
- System.out.println( k[l]+" ");
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- int a[]= {2,4,6,9,10,20};
-
- //if Array is not sorted :To sort array use Arrays.sort(a);
-
- findMissingNumber(a);
-
-
- }
- }
- Change the array in main method and practice try to find missing elements in an array that contains 1 to 100 numbers.