- Polymorphism means defining multiple methods with same name.
- Two types of polymorphism
1.Static polymorphism
2.Dynamic polymorphism.
Static polymorphism:
- Defining multiple methods with same name and with different type of arguments is known as static polymorphism.
- We can achieve this static polymorphism using method overloading.
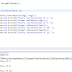
- package com.instanceofjava;
- class A{
- public void show(int a){
- System.out.println("saidesh");
- }
- public void show(int a,int b){
- System.out.println("ajay");
- }
- public void show(float a){
- System.out.println("vinod");
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- A a=new A();
- a.show(10);
- a.show(1,2);
- a.show(1.2);
- }
- }
- saidesh
- ajay
- vinod
Dynamic polymorphism:
- Defining multiple methods with same name and with same signature in super class and sub class.
- We can achieve dynamic polymorphism by using method overriding concept in java.
- Define a method in super class and override same method with same signature in sub class
- Whenever we call the method on t the object based on the object corresponding class method will be executed dynamically.
- package MethodOverridingExamplePrograms;
- public class Vehicle{
- void Start(){
- System.out.println("Vehicle started")
- }
- }
- package MethodOverridingExamplePrograms;
- public class Car extends Vehicle{
- void Start(){
- System.out.println("Car started")
- }
- }
- package MethodOverridingExamplePrograms;
- public class Bus extends Vehicle{
- void Start(){
- System.out.println("Bus started")
- }
- }
- package MethodOverridingExamplePrograms;
- public class Bike extends Vehicle{
- void Start(){
- System.out.println("Bike started")
- }
- }
- package MethodOverridingExamplePrograms;
- public class Test{
- public static void startVehicle(Vehicle vh){
- vh.start();
- }
- }
- In the above example based on the object creation at run time corresponding class method will be executed.
Bagikan
Dynamic polymorphism in java with example program
4/
5
Oleh
Kris Kimcil